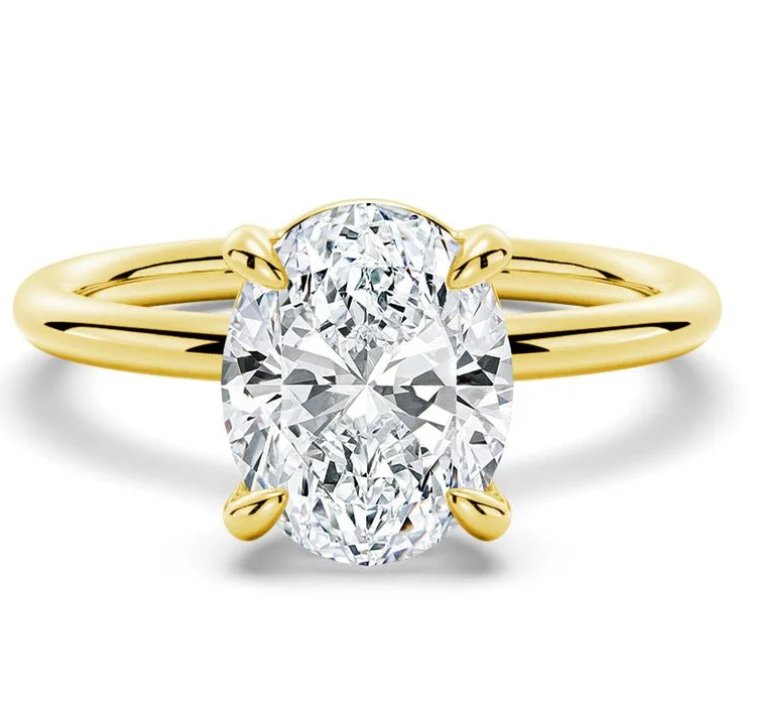
Moissanite and lab-grown diamonds are both popular alternatives to natural diamonds for various reasons, including ethical concerns, cost, and environmental considerations. Here are the key differences and similarities between the three:
Chemical Composition and Structure:
Moissanite: Moissanite is a naturally occurring mineral, but the moissanite used in jewelry is typically lab-created. It is composed of silicon carbide (SiC) and has a different crystal structure compared to diamonds.
Lab-Grown Diamonds: Lab-grown diamonds are created using advanced technological processes that replicate the conditions under which natural diamonds form. They have the same chemical composition (pure carbon) and crystal structure as natural diamonds.
Natural Diamonds: Natural diamonds are primarily composed of carbon atoms arranged in a crystalline structure known as diamond cubic. Each carbon atom is bonded to four other carbon atoms in a tetrahedral arrangement, resulting in a remarkably strong and stable structure.
Hardness and Durability:
Moissanite: Moissanite is very hard and scores 9.25 on the Mohs scale of hardness, making it suitable for everyday wear.
Lab-Grown Diamonds: Lab-grown diamonds are also extremely hard, scoring a 10 on the Mohs scale, which is the highest rating possible and the same as natural diamonds.
Natural Diamonds: Natural diamonds rank as the hardest mineral on the Mohs scale with a rating of 10, while moissanite is slightly lower with a rating of 9.25. Lab-grown diamonds share the same hardness as natural diamonds.
Brilliance and Sparkle:
Moissanite: Moissanite exhibits a different kind of brilliance and fire compared to diamonds. It tends to have more rainbow-like flashes of color due to its different optical properties.
Lab-Grown Diamonds: Lab-grown diamonds have a similar brilliance, fire, and sparkle to natural diamonds since they share the same crystal structure and refractive index.
Natural Diamonds:The brilliance and sparkle of a diamond are attributed to its ability to refract and reflect light. The facets cut into the diamond's surface act as mirrors, bouncing light internally and dispersing it back through the top of the stone. This play of light creates the dazzling sparkle and brilliance that diamonds are famous for.
Color and Clarity:
Moissanite: Moissanite is available in various grades, including colorless to near-colorless options. It typically has fewer inclusions and flaws compared to natural diamonds.
Lab-Grown Diamonds: Lab-grown diamonds come in a range of colors and clarities, similar to natural diamonds. They can be found in various qualities, from internally flawless to included.
Natural Diamonds: Diamonds occur naturally in a variety of colors, ranging from colorless to various shades of yellow, brown, and even rare hues like blue, pink, or red. The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) grades diamonds on their color and clarity, with colorless diamonds (graded D-F) and internally flawless stones fetching the highest prices due to their rarity and beauty.
Cost:
Moissanite: The price is more budget-friendly, Moissanite typically presents a more affordable alternative compared to natural or lab-grown diamonds. However, even with its lower price, Moissanite still exhibits a dazzling sparkle comparable to diamonds, making it an ideal choice for consumers seeking a diamond-like appearance at a lower cost.
Lab-Grown Diamonds: Lab-grown diamonds are often priced lower than their natural counterparts but are generally more expensive than moissanite due to the production process and their closer resemblance to natural diamonds.
Natural Diamonds: The cost of natural diamonds can vary widely depending on factors such as carat weight, color, clarity, and cut quality. Larger, high-quality diamonds command higher prices, with rare and flawless stones fetching astronomical sums at auction.
Ethical and Environmental Considerations:
Moissanite: Lab-created moissanite is considered a more ethical and environmentally friendly option compared to natural diamonds, as it doesn't involve mining or the associated environmental and ethical concerns.
Lab-Grown Diamonds: Lab-grown diamonds are also considered a more ethical and environmentally conscious choice since they avoid the issues associated with traditional diamond mining.
Natural Diamonds:Ethical and environmental concerns arise from natural diamond mining due to labor practices and environmental impact. Lab-grown diamonds are increasingly seen as a more ethical and eco-friendly alternative, given their lower energy use and lack of mining involvement. Nonetheless, ensuring their ethical and sustainable production remains crucial.
In summary, moissanite, lab-grown diamonds, and natural diamonds each have their own distinct characteristics. Moissanite and lab-grown diamonds share similarities in their ethical and environmental benefits, such as reduced environmental impact and ethical concerns compared to natural diamonds. However, they differ in terms of their chemical composition, brilliance, and cost. Natural diamonds, on the other hand, have a unique geological origin and are highly valued for their rarity and enduring appeal.
The choice between moissanite, lab-grown diamonds, and natural diamonds ultimately depends on individual preferences and priorities, whether it be ethical considerations, budget constraints, or the desire for a gemstone with a natural origin and historical significance.